
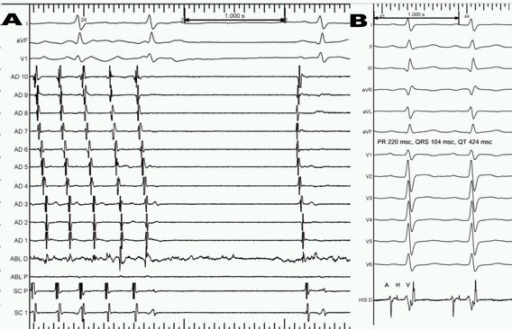
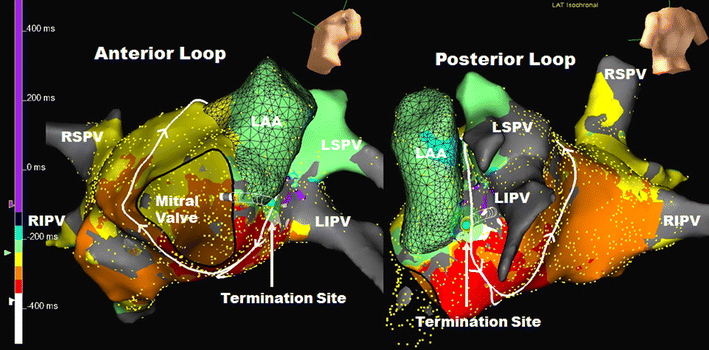
Although there are various techniques, this is the most common technique for surgical ablation. This procedure is also referred to as Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. The heart must be stopped and a heart-lung machine used for the Cox-Maze Procedure. This creates scar tissue that stops electrical activity from passing through the upper chambers. These incisions will then be sutured (sewn) together. Physicians will make a precise pattern of incisions (cuts) inside the upper chambers of the heart (the right and left atria). Others can be performed on a beating heart and do not require the use of a heart-lung machine (“off-pump” ablation). Some procedures require that the heart be stopped and the patient be put on a heart-lung machine (referred to as “on-pump” ablation). There are two main types of surgical ablation. If you smoke, you should stop at least two weeks before your surgery, as smoking can contribute to blood clotting and breathing problems. To reduce the risk of vomiting while asleep, you will be asked not to eat or drink after midnight the night before surgery. Surgical ablation is performed under general anesthetic – in other words, you will be asleep throughout the procedure. There are two main ways in which ablation can be performed: surgically or by catheter (nonsurgically).Īlthough less common, surgical ablation may be combined with other open-heart surgeries, such as bypass surgery or heart valve repair or replacement. Many abnormally fast heart rhythms are triggered by areas of abnormal heart tissue that cause the electrical system of the heart to “short-circuit.” By ablating or destroying these areas, the scar tissue that forms helps to prevent this short-circuit and allows for a return to a normal regular heart rhythm. The goal is to restore a regular rhythm to prevent these conditions from occurring. Why is it done?Ībnormal heart rhythms known as arrhythmias can cause: Ablation may be used to treat a heart that beats too quickly (more than 100 beats per minute, a condition known as tachycardia), or a heart that beats so it contracts in an uncoordinated fashion, known as fibrillation. The pumping action of your heart is triggered by electrical impulses. Usually, the heart beats between 60 and 80 times a minute. Ablation is a procedure for restoring normal heart rhythm, particularly if the irregular rhythm has not responded to medication.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
